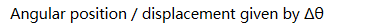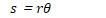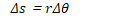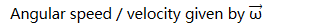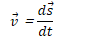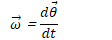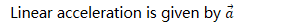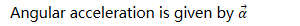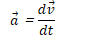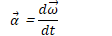Radians and Degrees
In degrees, once around a circle is 360°
In radians, once around a circle is 2π
A radian measures a distance around an arc equal to the length of the arc's radius
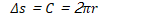
Linear vs. Angular Displacement
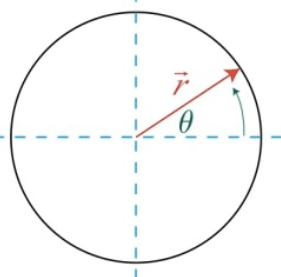
Linear vs. Angular Velocity
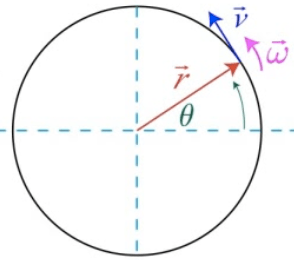
Direction of Angular Velocity
Converting Linear to Angular Velocity
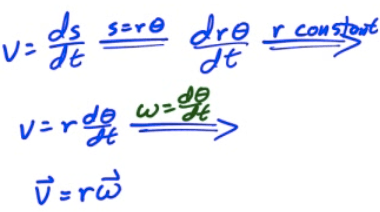
Linear vs. Angular Acceleration
Centripetal Acceleration
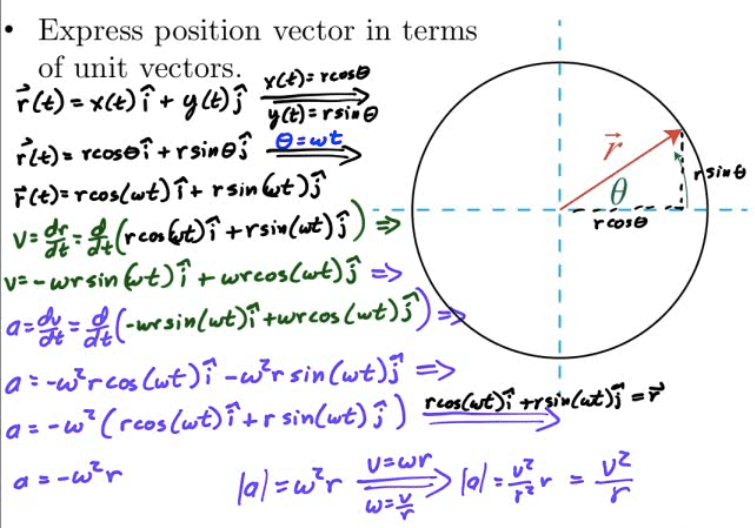
Reference Frames
A reference frame describes the motion of an observer
- Most common reference frame is Earth
Laws of physics we study in this course assume we're in an inertial, non-accelerating reference frame
There is no way to distinguish between motion at rest and motion at a constant velocity in an inertial reference frame
Calculating Relative Velocities
Consider two objects, A and B.
Calculating the velocity of A with respect of reference frame B (and vice versa) is straightforward
Example:
Speed of car with respect to the ground
Walking on a train, speed of a person with respect to the train
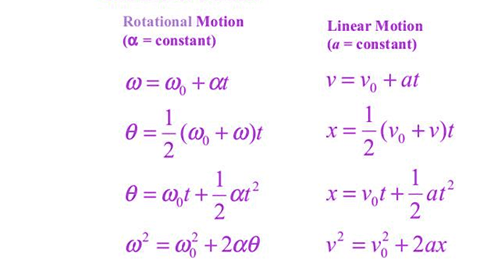
Linear vs. Angular